The Building Process of Renovating a Historic House
Renovating a historic house is both an exciting and challenging endeavor. The charm of historic homes lies in their unique architecture, craftsmanship, and the stories they tell. However, restoring these properties to their former glory while integrating modern comforts requires a thoughtful approach. Here’s a brief guide to understanding the building process involved in renovating a historic house.
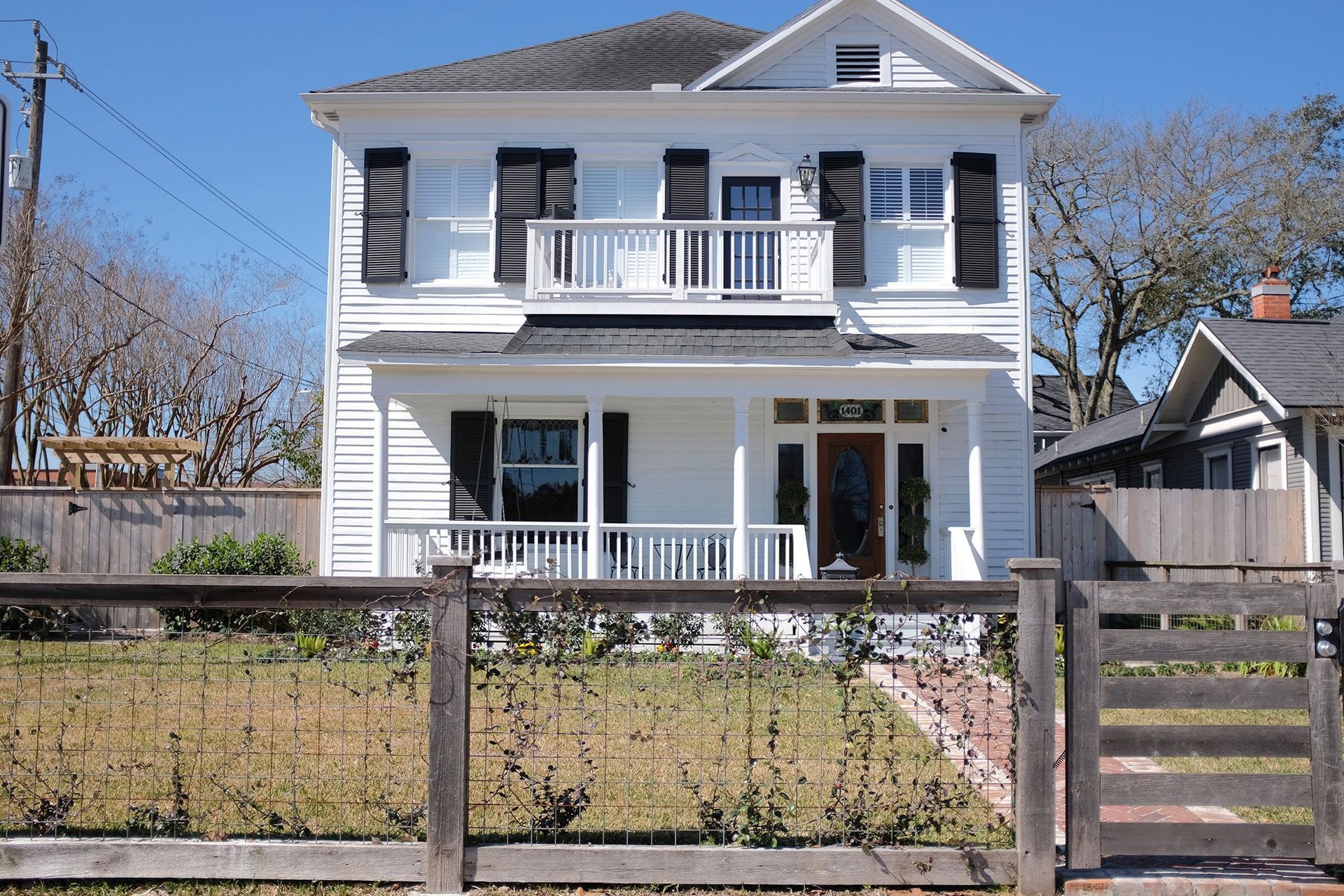

1. Understanding the Historic Significance
Research and Documentation
Start by researching the history of your home. Understand its architectural style, original features, and historical significance. This can involve digging into old photographs, historical records, and talking to local historians or preservation societies.
Preservation Guidelines
Familiarize yourself with local preservation guidelines and regulations. These rules are designed to protect the historical integrity of the property and ensure that renovations respect its original design.
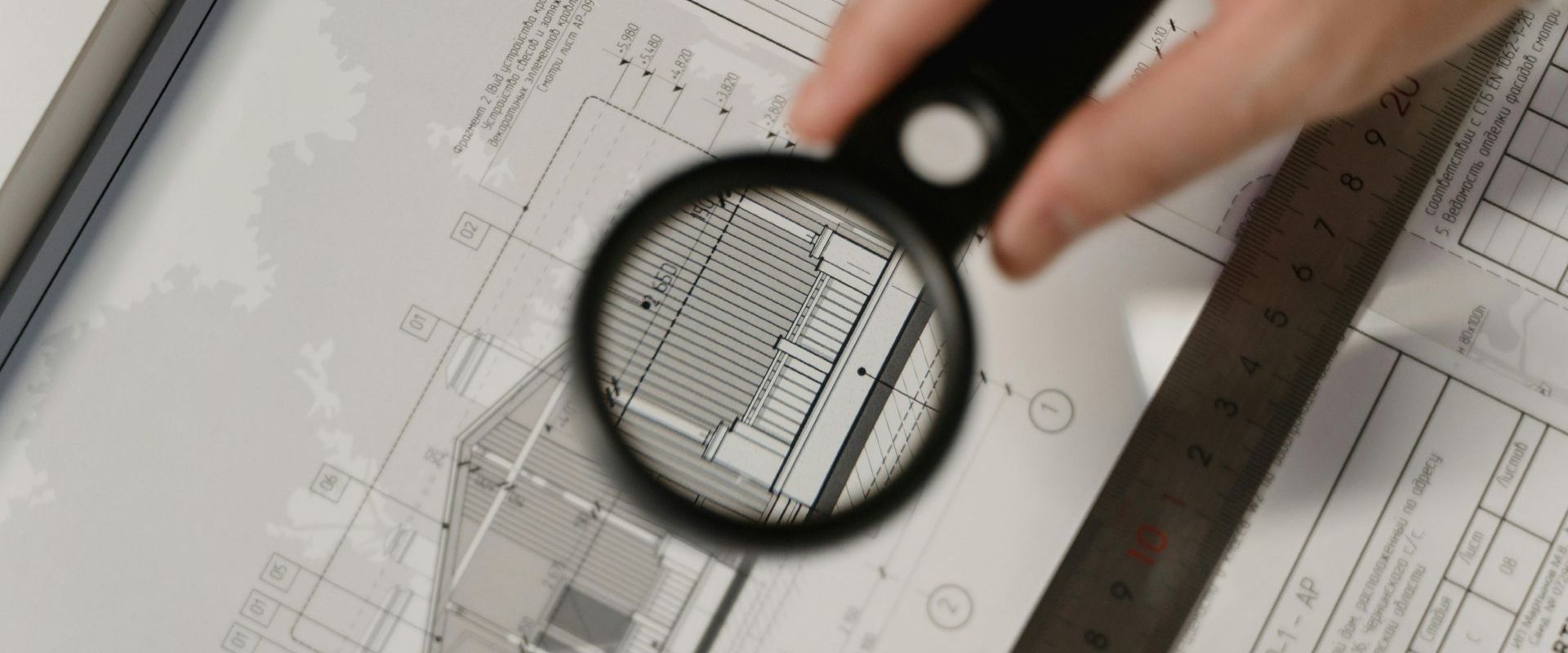

2. Planning and Design
Assessment
Hire a professional to conduct a thorough inspection of the property. This includes evaluating the structural integrity, electrical and plumbing systems, and identifying any issues like lead paint or asbestos.
Design Goals
Define your renovation goals. Are you looking to restore the house to its original condition, or are you aiming to blend modern updates with historic charm? Work with an architect or designer experienced in historic renovations to create a plan that balances these needs.
Approval and Permits
Obtain the necessary permits and approvals from local preservation boards or commissions. This step ensures that your renovation plans comply with historical preservation standards and local building codes.
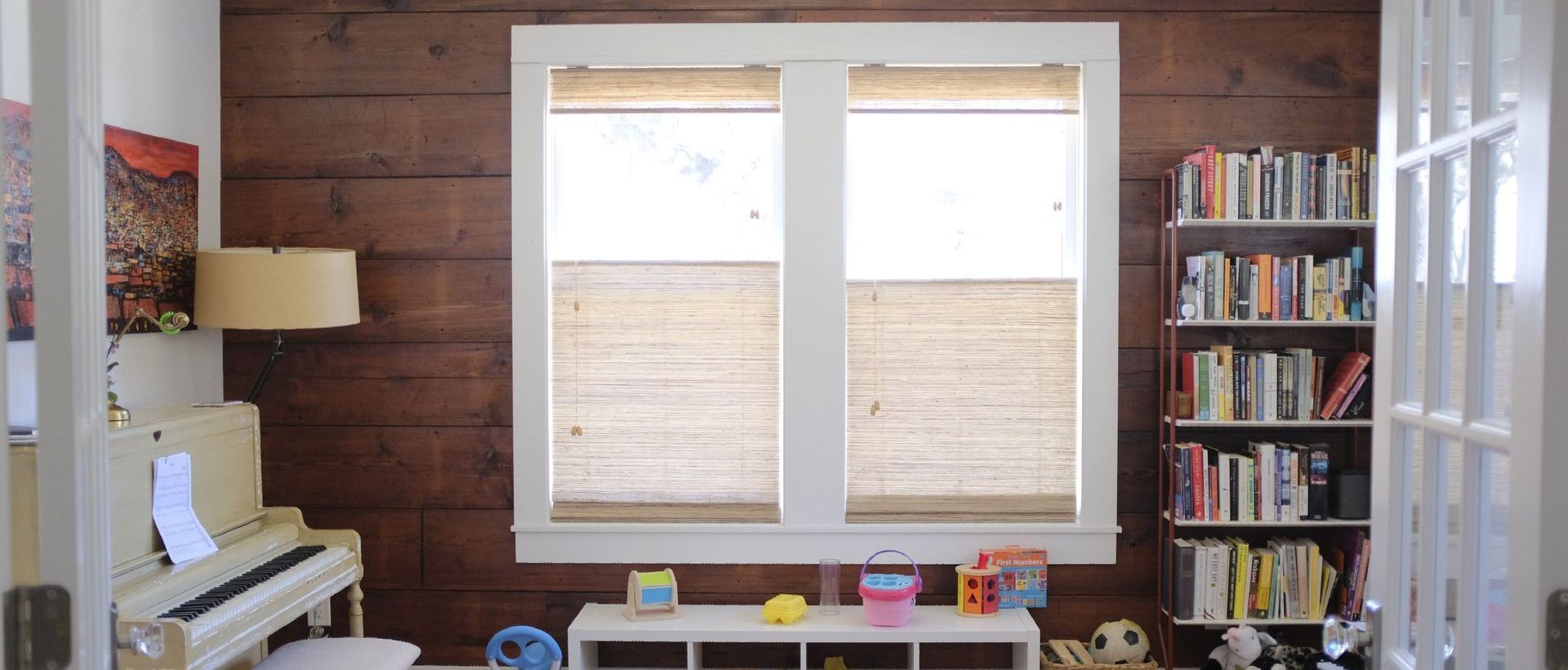

3. Preservation of Original Features
Restoration
Focus on preserving original features such as moldings, windows, and flooring. If these elements are damaged, repair or restore them using techniques and materials that match the original.
Materials
Use historically accurate materials for any repairs or replacements. For example, if your home has original wood siding, source similar wood for repairs to maintain consistency in appearance.
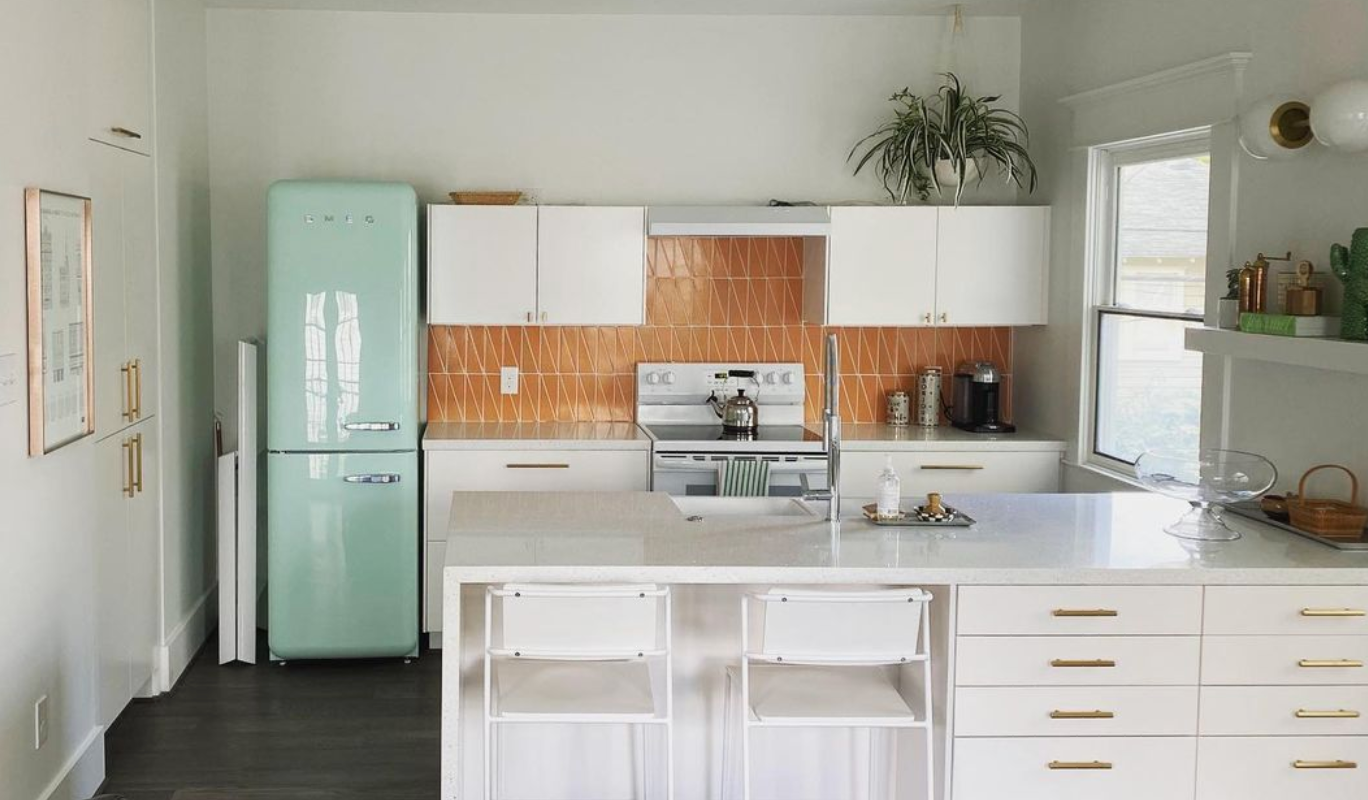

4. Modernization and Upgrades
Systems Updates
Update essential systems like plumbing, electrical, and HVAC to meet modern standards. This should be done in a way that minimizes disruption to the home’s historical features.
Integration
When incorporating modern amenities, do so in a way that complements the historic character. For instance, you might add modern insulation or energy-efficient windows but choose designs that blend with the original architecture.
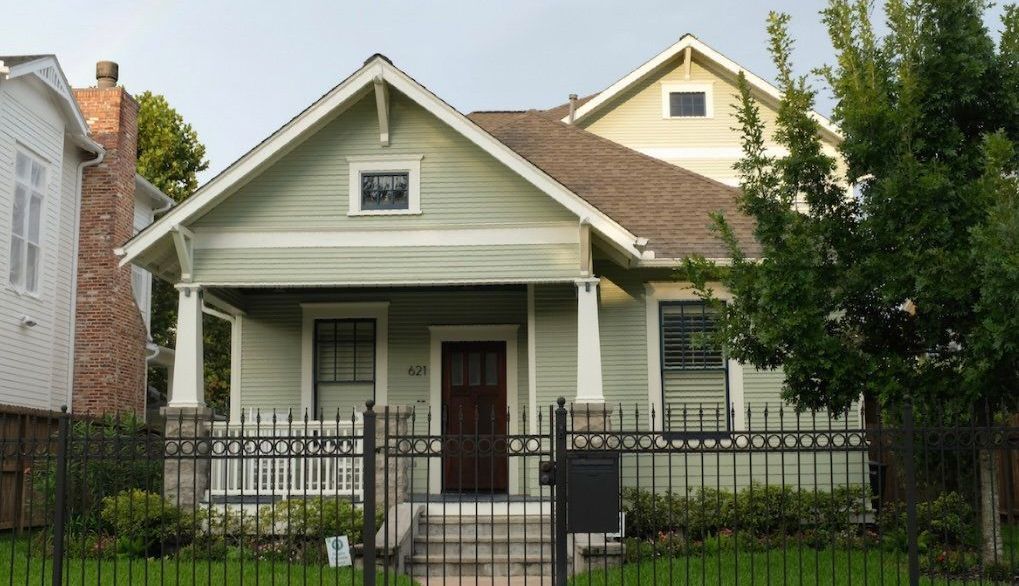

5. Construction and Restoration
Contractor Selection
Choose contractors who have experience with historic renovations. They should understand the nuances of working on older homes and be able to execute repairs and updates with care.
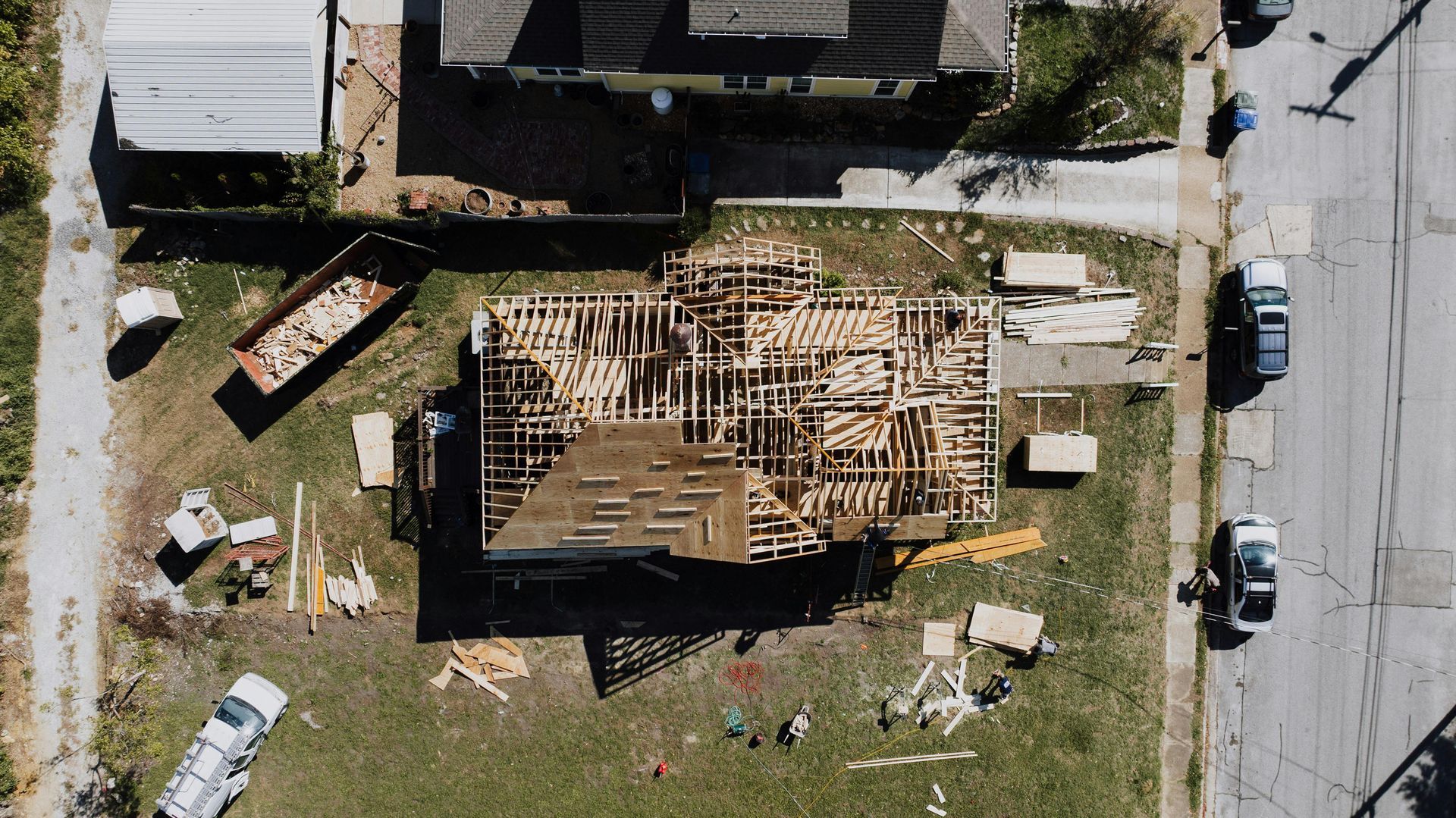
Building Process
The construction phase involves executing the renovation plan while carefully monitoring progress to ensure compliance with preservation guidelines. Regular site visits and inspections can help catch any issues early.
Historic Detailing
Pay attention to the details during the restoration process. This includes replicating intricate moldings, restoring original hardware, and ensuring that new elements seamlessly integrate with the old.

6. Final Touches and Clean-Up
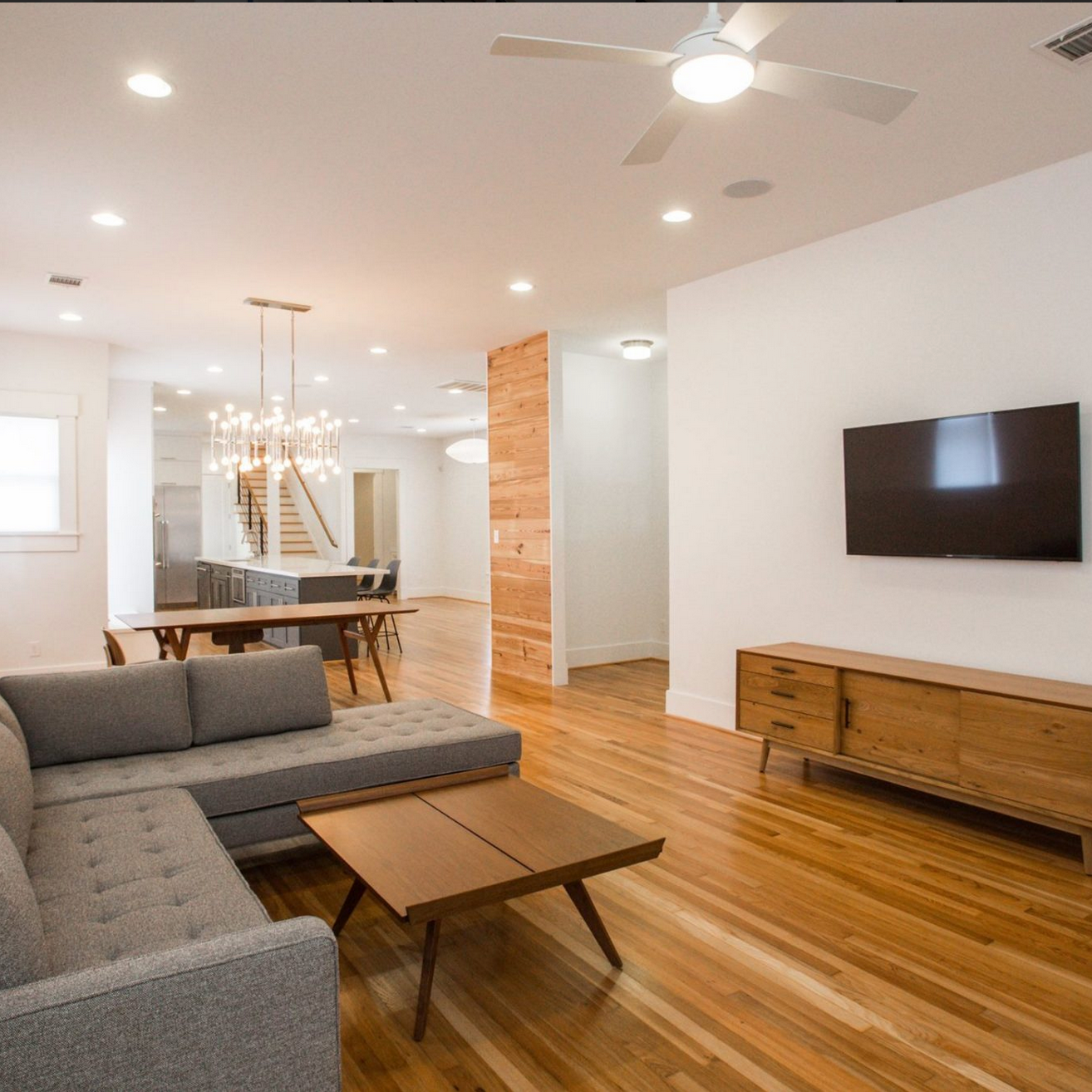
Finishing Touches
Complete any final touches, such as painting, refinishing floors, and installing historically accurate fixtures. These details help bring the renovation to completion and enhance the home's overall aesthetic.
Clean-Up
Thoroughly clean the site and address any remaining issues. This ensures that the home is ready for occupancy and that the renovation respects the historical integrity of the property.

7. Preserving and Celebrating History
Documentation
Document the renovation process and the historical features of the house. This information can be valuable for future owners and for maintaining the historical narrative of the property.
Community Engagement
Consider sharing your renovation story with the community. Local historical societies or neighborhood groups might be interested in learning about the project and how you’ve contributed to preserving the area’s heritage.

Conclusion
Renovating a historic house is a rewarding journey that requires careful planning, respect for the past, and a commitment to quality craftsmanship. By understanding the building process and following these steps, you can restore your historic home to its former glory while preserving its unique character for future generations to enjoy.
Whether you're a homeowner embarking on a personal renovation project or a professional working in the field, embracing the challenges and joys of historic preservation can lead to stunning results that honor both the past and the present.